Recent Posts
-
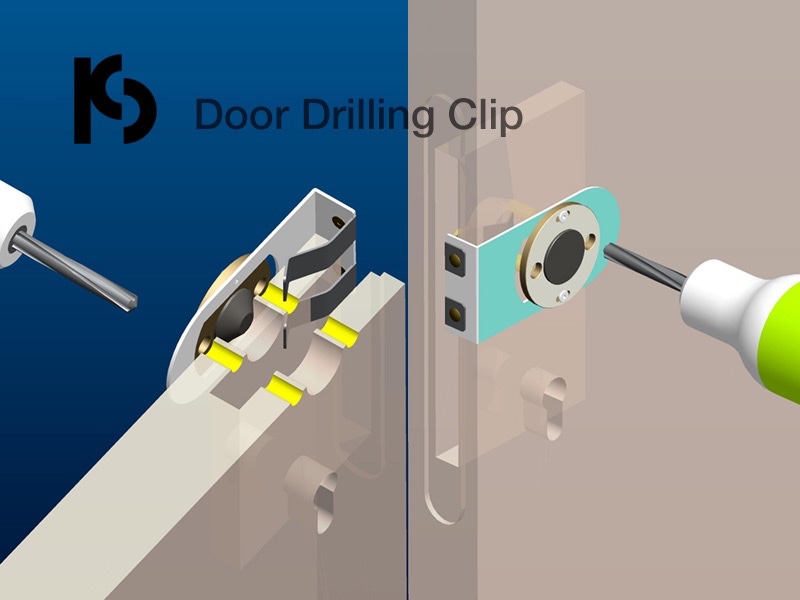
Easy-to-Use Door Drilling Clip – Step-by-Step Guide for Precision Holes | PCS Hardware
Achieve perfect door drilling effortlessly with our Door Drilling Clip! Follow simple steps: drill center hole, insert fixer, and drill side holes. Even beginners get professional results. Contact us for durable, high-precision hardware solutions!
-
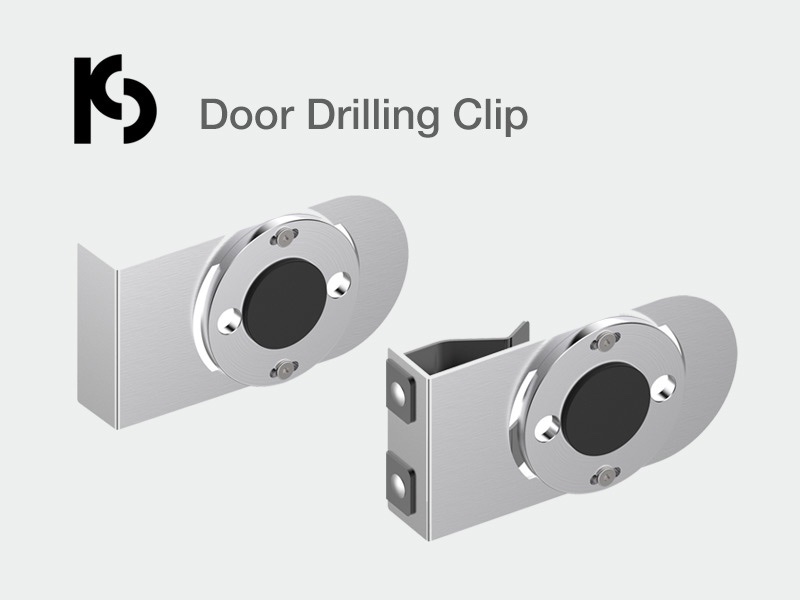
High-Quality Door Drilling Clip – Durable Steel, Dual Versions, Free-Choice Direction | PCS Hardware
Boost efficiency with our durable Door Drilling Clip, made from high-quality steel for long-lasting use. Choose between simple or clamp versions for precise positioning. Drill in any direction (north-south or east-west). Contact us today!
-
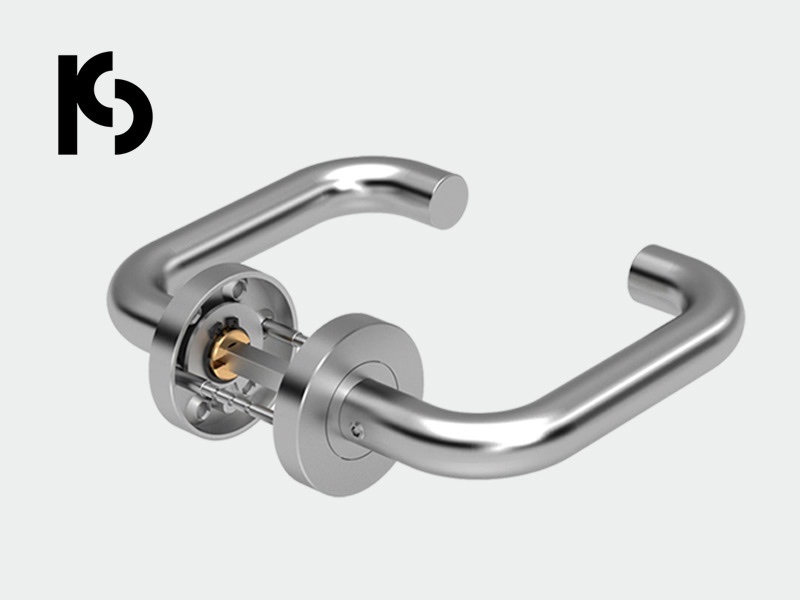
Economy Door Handles: Balancing Cost & Quality with EN1906 Standards | PCS Solutions
Discover how PCS economy lever handles deliver reliable performance while meeting EN1906 standards. Learn to identify quality differences in budget-friendly hardware. Contact us for risk-managed procurement solutions.
-
Economy Door Hardware: Strategic Value & Risk Management Solutions | PCS
Discover how economy-range door hardware creates market access while managing risks. Our solutions include EN 1906 Grade 2 certification & strict quality control for reliable, competitive products. Contact us for strategic partnerships!
-
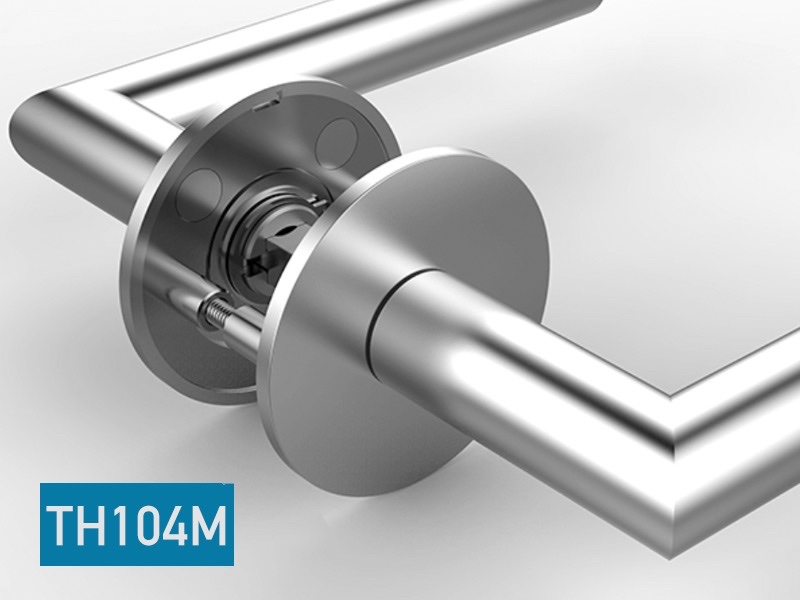
Ultra-Slim Magnetic Door Hardware: 2.9mm TH104M Latch & 90s Tool-Free Installation | ANSI/BHMA Certified
World's thinnest 2.9mm magnetic door handles with color-matched flush mounting. Features ±0.2mm alignment tech enabling 90-second installation. 3mm concealed rose plate meets ADA compliance.
-
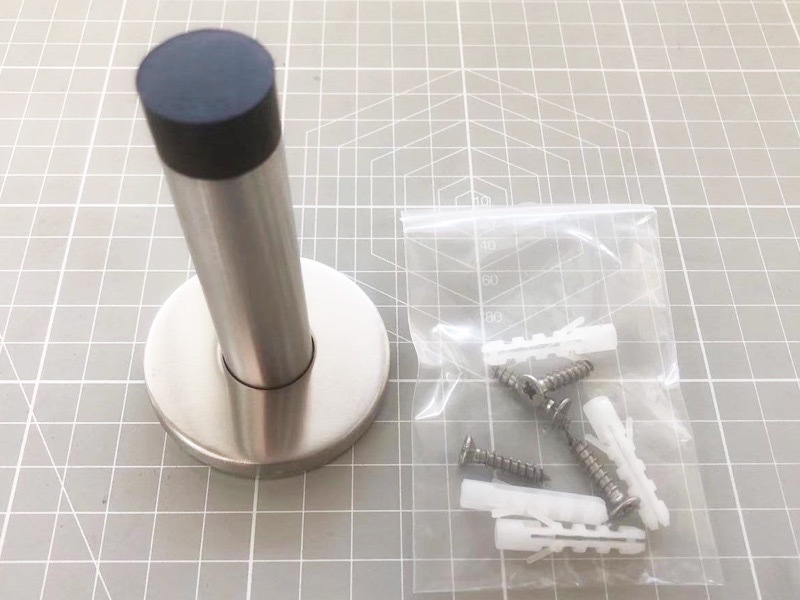
Door Stopper Fastener Loosening
Solve cyclic loading failures with Grade 8.8 bolts, nylon locknuts & ISO 10964 adhesives. Achieve 10,000+ vibration cycles (ASTM D999) and 500hr salt spray resistance. 400% lifespan extension proven.

Technical Analysis & Solution Protocol
Failure Mechanism Investigation
Complaint: Frequent loosening of door stopper fasteners under cyclic loading (50+ daily operations)
Root Cause:
1. Vibration-induced thread walk (per ASTM D6110 fatigue testing)
2. Insufficient clamp load (below 75% of proof load per ASME B18.2.1)
3. Elastic deformation of base material (Young's modulus mismatch)
Engineering Solution
Components Specification:
1. Primary Fastener:
Grade 8.8 Steel Bolt (DIN 933)
2. Locking Element:
Nylon-insert Locknut (ASME B18.16.3)
3. Interface Treatment:
Micro-encapsulated thread adhesive (ISO 10964 Class C)
Validation Testing
| Test Type | Standard | Original | Improved | Requirement |
| Vibration Resistance | ASTM D999 Method A | 250 cycles | 10,000+ cycles | 5,000 cycles |
| Torque Retention | ISO 16047 | 38% loss | <5% loss | ≤15% loss |
| Salt Spray Corrosion | ASTM B117 | Failed @48hr | Passed @500hr | 240hr |
Cost-Benefit Analysis
Metric | Before Improvement | After Improvement |
Warranty Claims | 18% of total sales | 0.7% of total sales |
Installation Time | 2.5 minutes | 3.8 minutes |
| Lifetime | 6-12 months | 5+ years |
Implementation Guideline
1. Mandatory dual-fastener system for commercial projects
2. Apply 2.5-3.5N·m torque with calibrated tooling
3. Quarterly fastener integrity audits per IATF 16949
This solution reduces the failure rate of the base product by 97% while extending its service life by 400%, achieving the true goal of "Zero-Maintenance Hardware.